Data Privacy in SaaS: Best Practices for SaaS Security
In today's world, companies are turning to various cloud providers for their software needs, which has made Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) extremely popular. SaaS is a cloud-based software delivery framework that enables end consumers to access software applications via the Internet. The software is hosted on remote servers, maintained and updated by the service provider, and made available to clients via web browsers, mobile applications, and APIs.
SaaS offers several advantages over traditional software delivery models, including lower initial costs, scalability, adaptability, and accessibility. Since the software is hosted on the service provider's servers, users do not need to invest in costly infrastructure to use it. To access the software as an on-demand saas service provider, end consumers instead pay a subscription fee.
SaaS provides easy access to software applications minus the need for complicated infrastructure. Nevertheless, data privacy and security are of the essence for SaaS owners. Data privacy in SaaS revolves around safeguarding sensitive data saved and handled within the SaaS platform, saas security concerns such as protection against unauthorized access and misuse.
Understanding Data Privacy in SaaS
Using SaaS technology, sensitive data can be stored and processed confidentially. SaaS companies utilize methods, policies, security tools, and technology to protect user data. Data privacy includes preventing illegal access, disclosure, change, or destruction. Let's take a look at the data issues SaaS owners face in the next section.
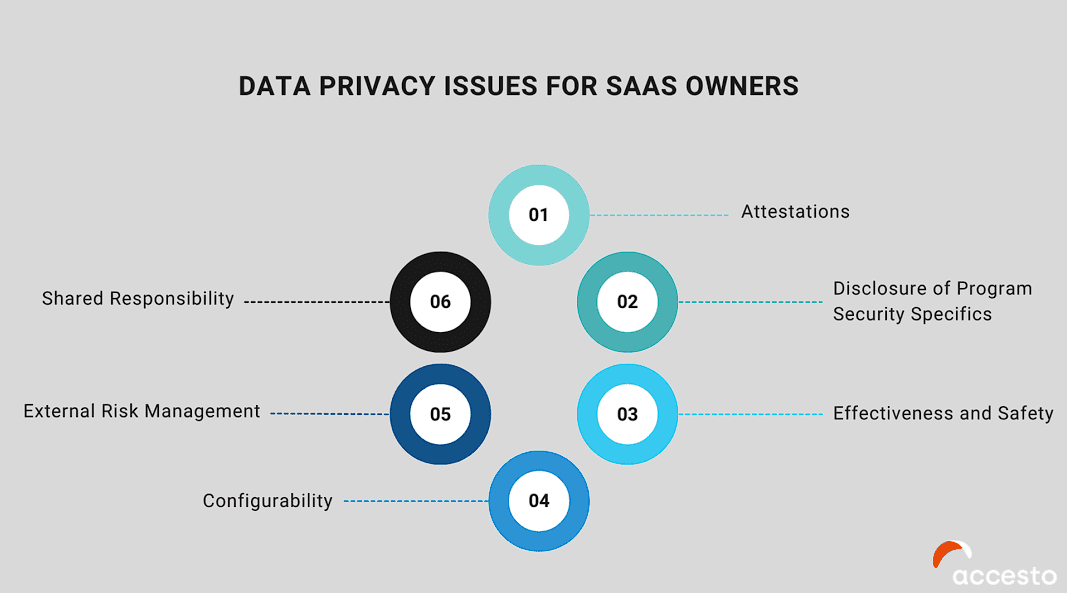
Data privacy issues for SaaS owners:
SaaS providers face unique challenges in meeting customer expectations and maintaining the efficiency of their products and services while safeguarding huge amounts of customer data accessible from various devices.
Here are some key areas where they encounter these challenges:
Attestations
Finding the right balance between external attestations/certifications, cost, and time is crucial for SaaS providers. Customers want assurance regarding critical information security and privacy controls, such as access management, change management, encryption, and staff qualifications. SaaS providers must identify and commit to the relevant attestations, such as SOC 1, SOC 2, and ISO certifications.
Disclosure of Program Security Specifics:
The providers often need help to balance sharing enough information to satisfy customer needs and protecting their environment from potential cyber-attacks. A high level of information sharing can increase vulnerability, while a low level of information sharing can increase customer resistance. Providers should conduct risk assessments, benchmark customer requests and security teams, and perform cost-benefit analyses to determine the optimal level of information sharing.
Effectiveness and Safety
SaaS providers constantly aim to balance scalable growth with mitigating risks associated with shared environments. Implementing robust controls to prevent data leakage between customers can be challenging and costly. Providers must conduct comprehensive risk analyses to gain senior management support to identify the most significant risk factors. In some cases, bringing in external experts may be necessary to highlight these risks.
Configurability
Developing a SaaS platform with comprehensive configuration and adaptability is vital to minimize the need for future customization. Customization increases platform complexity and makes it more challenging for enterprise security to ensure no vulnerabilities.
External Risk Management
SaaS providers often face extensive requests from organizations storing personally identifiable information (PII) regarding their security measures. To respond efficiently to customer requests through third-party risk management programs, providers should demonstrate available cyber and physical security audits and provide a formal security posture statement. This approach reduces the provider's burden and saves customers time obtaining essential security information.
Shared Responsibility
To minimize vulnerabilities in SaaS infrastructure, customers and providers must define their respective responsibilities. Shared responsibility models ensure accountability and comprehensive protection of sensitive customer data while clearly defining SaaS security, privacy, regulatory compliance, and operational activities.
By addressing these concerns, SaaS owners can improve data privacy, limit risks, and provide their clients with a safe and trustworthy platform.
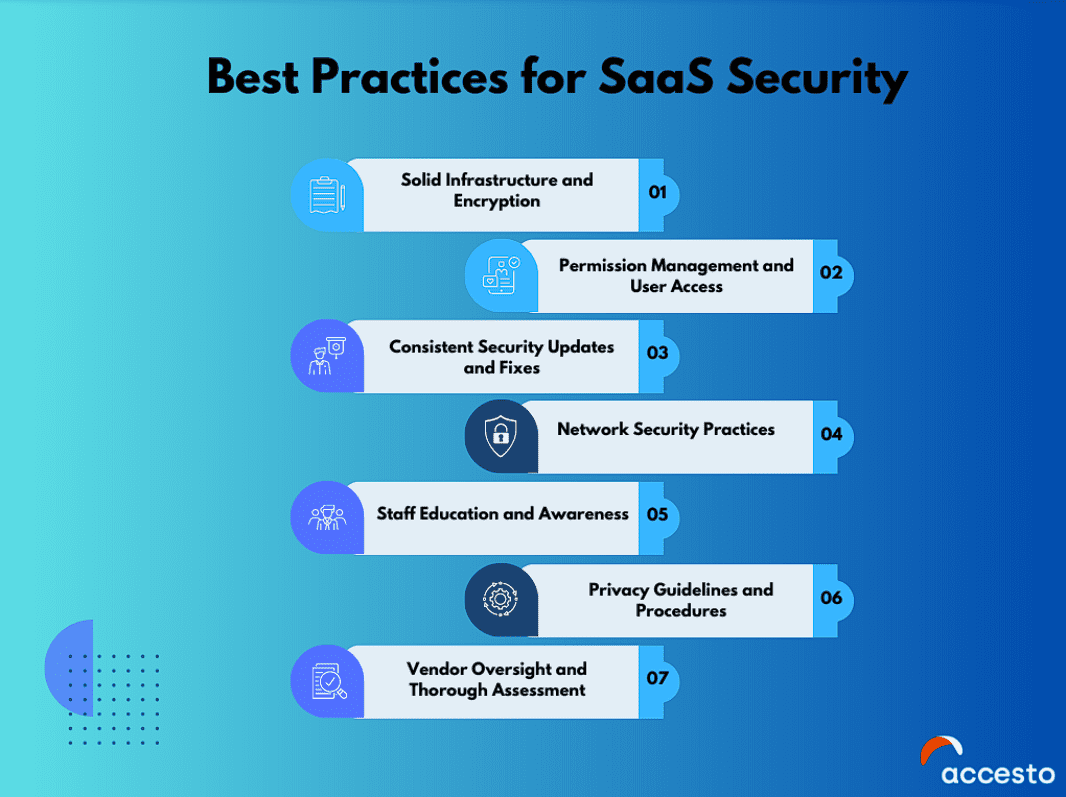
Best Practices for SaaS Security
In light of the challenges SaaS owners often encounter regarding data privacy, it is crucial to recognize that there are effective strategies to mitigate data security and privacy concerns. By implementing industry best practices, SaaS owners can establish robust safeguards to protect sensitive information. Here are several key recommendations for SaaS owners to consider when it comes to data privacy.
Solid Infrastructure and Encryption
Building secure SaaS apps demands a resilient infrastructure and powerful encryption mechanisms. SaaS providers can shield sensitive information from unauthorized access by adopting widely accepted encryption algorithms and secure communication protocols. The SaaS platform should use encryption methods to secure sensitive data when it is stored and transmitted, including in databases and files.
Since cloud applications cannot rely on conventional SaaS security measures such as firewalls, they must rely on data encryption and key management. Customers are uneasy about entrusting this vital task to data vendors and prefer to manage their keys personally. Using Transport Data Encryption (TDE), data "in motion" can be protected. However, other data transfers via HTTP or FTP can be risky, so they should be secured with Transport Layer Security (TLS).
Permission Management and User Access
Cloud users can access different sections of the same cloud infrastructure according to their duties and permissions. Since SaaS operations are accessed online, hackers need only your credentials to access the account. A detailed access control system is essential to maintaining data privacy.
By setting up role-based access control (RBAC), SaaS providers can restrict user permissions and grant access solely to relevant data and features. Set up robust multi-factor authentication methods, such as two-factor authentication (2FA), to improve account SaaS security. Users must supply an extra authentication factor like a unique code sent to their mobile device for added protection.
In addition, strong identity and access management (IAM) policies are crucial to the security of SaaS and public cloud services. An Identity and Access Management system regulate permissions and access to cloud resources. IAM best practices include:
- Getting rid of inactive accounts
- Providing access to users who need it.
- Implementing robust password policies
Consistent Security Updates and Fixes
The SaaS platform needs to be updated in terms of security patches and updates. Vendor-supplied software updates should be applied systematically by SaaS providers to address vulnerabilities and security gaps. Security audits and vulnerability assessments help detect potential security risks and enable prompt mitigation. Moreover, by performing routine Vulnerability Assessment and Penetration Testing, you can identify SaaS security flaws in your SaaS applications.
As part of SaaS security practices, a SaaS provider should conduct regular penetration tests to ensure that its web application is not vulnerable to mass attacks. An effective method of evaluating SaaS security is to engage a VAPT provider since it reduces your workload and ensures that your systems are evaluated in a failsafe manner.
Network Security Practices
For SaaS data privacy, it is crucial to implement network security practices. There are two types of network security governance in SaaS services: controls owned and operated by SaaS providers and controls a SaaS consumer may wish to consider. In order to ensure network security, it is crucial to consider Zero Trust Network Access (ZTNA) and Secure Access Service Edge (SASE).
Moreover, use reliable Virtual Private Networks (VPNs) for secure communication channels and safeguard data during transfer. Employ firewalls and intrusion detection systems (IDS) to oversee and regulate network traffic, detect possible intrusions, and effectively counteract malicious activities.
Staff Education and Awareness
Data privacy and SaaS security best practices must be taught to employees. To foster a SaaS security-aware culture, hold regular training sessions focusing on data privacy, phishing attacks, social engineering, and secure data handling. Increase awareness of common SaaS security threats, and offer guidance on identifying and addressing them to reduce data breach risks.
Whenever you onboard new customers or send critical updates to existing ones, ensure that you actively inform people of the impact on their business-critical data that breaches their SaaS security. Most consumers do not comprehend the implications of increasing SaaS companies shifting to a cloud-based infrastructure. Ensure your consumers know how to secure their information to reduce SaaS security issues.
Privacy Guidelines and Procedures
Creating and enforcing extensive data privacy guidelines is key for SaaS service providers. These guidelines should cover data handling, access, consent management, disaster recovery, retention, and breach response procedures. Communicate these guidelines to staff, clients, and other stakeholders to ensure everyone understands their data privacy responsibilities.
Vendor Oversight and Thorough Assessment
Providers must scrutinize their SaaS security measures and capabilities when collaborating with SaaS vendors. Assess factors like data protection methods, security certifications, incident response capacity, and compliance with privacy regulations to confirm vendors prioritize data security team privacy. Contracts should explicitly state the expectations for data privacy and security, including handling, confidentiality, and third-party access, as well as breach notifications.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
Neglecting Shared Security Responsibility:
It's a common mistake to think that only the SaaS service provider is accountable for SaaS security. Data security must be recognized as a shared responsibility model, where both the provider and the customer cooperate to keep the data safe. SaaS providers can contribute to data security solutions' privacy by being actively involved in securing data, following best practices, and adhering to security policies and guidelines.
Not Conducting Regular Security Audits:
Regular security audits and assessments are essential for business continuity and should not be noticed. These audits identify vulnerabilities, assess SaaS security measure effectiveness, and ensure compliance with industry standards and regulations. Consistent security audits enable SaaS owners to detect and address risks proactively, improving data privacy and overall security.
Poor Incident Response Planning:
A well-designed incident response plan is crucial during security breaches or incidents. SaaS owners should develop a thorough plan outlining actions, defining roles and responsibilities, and establishing clear communication channels. Swift and effective responses to security incidents help the SaaS platform minimize impact and potential damages.
Conclusion
Ensuring data privacy and security is crucial for SaaS owners in today's digital landscape. By implementing best practices such as solid infrastructure and encryption, permission management and user access control, consistent security updates, network security practices, staff education and awareness, privacy guidelines and procedures, and thorough vendor oversight, SaaS owners can establish robust safeguards to protect sensitive information. Additionally, avoiding common mistakes such as neglecting shared security responsibility, not conducting regular security audits, and poor incident response planning is essential. Prioritizing data privacy and security not only ensures compliance with regulations but also builds trust and confidence among customers, making the SaaS platform a safe and reliable choice for software needs in the modern era.