What you should know about UX design processes
Building good products in a fast-changing and competitive world involves several different issues that need to be addressed for a product to be noticed and give users the right feeling. As a result, UX design, as it is called, is not just a buzzword in today's high-tech world but a significant and integral part of creating solutions that win in demanding markets.
Today's article will focus on UX design, its processes and tools, why it is so important, and why developers should understand it.
What is UX?
Before we dive into the story of UX design, it is worth focusing on the first word - UX. It refers to the phrase 'user experience,' i.e., what kind of interaction a user has with a product. For example, when someone drives a car, there is an interaction between the driver and the car's various components.
Therefore, all vehicle design elements, such as colour, equipment, or interior design, impact the driver's experience. They, therefore, play an essential role in how this user feels about the product.
What is UX design?
UX design can be described as a process that design teams use to help IT build a robust product that gives users tangible value and a relevant experience. It is said that UX designers design the user experience, which is somewhat symbolic, as these specialists create the right conditions for users to perceive the interaction with an application in the right way.
Thus, it's better to say UX designers design for UX.
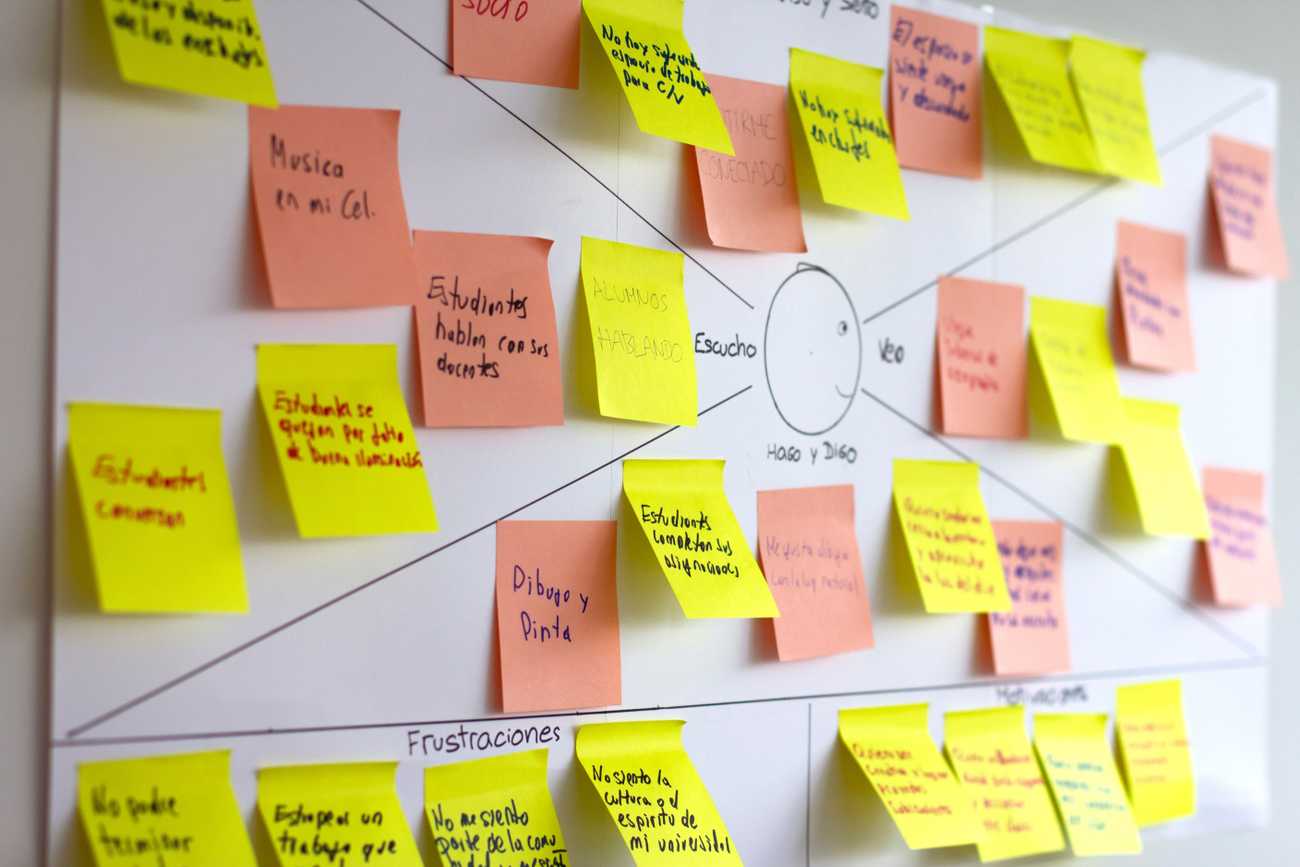
A critical issue in UX design is to build a product that is not only practical but also usable. It was well put by Peter Morville of Semantic Studios, who divided an excellent product into seven qualities or, as he called them - facets:
Useful
No matter how vital the other qualities are, a product should always be useful for the user. Therefore, in developing our knowledge and skills in UX design, we should always strive to make our innovations functional.
Usable
Usability is essential in web design, but more is needed. Human-computer interaction methods cover only some aspects of web design.
Desirable
In the design process, we should always consider and satisfy the clients expectations towards the brand identity, image, and other elements involving emotion.
Findable
Users should always be able to find what they are looking for by using the solution. Consequently, all objects and navigations should enable them to do so.
Accessible
It is important to remember that users are different. Just as facilities such as lifts and ramps are introduced in the physical world, apps should be designed to make it as easy for people with disabilities to use them.
Credible
An essential element of a solid UX design process is that the company and its products are trustworthy. The better the ratings, the better the reception from the target audience.
Valuable
A precious element is a value that the application builds for the user. In the case of a not-for-profit organization, the user needs to feel that the app is helping them advance their mission. When it comes to businesses, the solution should support the customer's bottom line and increase customer satisfaction.
UX designers know these things
A few more critical points about UX design are worth keeping in mind.
It's all about people
We should remember that it is, after all, people who use the application, so the solution should be designed to meet their expectations and respond to their specific needs. UX design requires considering issues such as needs, wants, and the context in which the user will want to use the application.
User experience is heavily geared toward what users feel and think because it is the human being, as an essential thinking and feeling being, who interacts with the final product. Therefore, their rational and emotional sides play a crucial role in how they perceive the product.
It is also worth remembering that a person's feelings about a product can change. Compared to how they looked at the product in the first minutes or hours, their perspective after some time may be completely different. It may be related to the fact that they are more familiar with the solution over time.
Remember the context
Another important consideration is the context in which the user will use the solution since every product is used for specific purposes and circumstances. At the same time, each app has a vital role in the user's life, as it helps them realize their goals, affecting other aspects of their life.
UX design is not UI design
One of the problems with UX design is that people confuse it with UI (User Interface) design. It is probably because the word "design" comes up, which brings to mind the visual side of the product. Yes, the interface is an integral part of the user experience. Still, it is just the outer layer of the solution, and the viewer's experience is made up of many more different factors.
Previously I wrote an article about designing a good UI, if you’d like to know more about it.
It's An ongoing process
As technology changes, so do trends, needs, and user expectations of new solutions. Therefore, it is worth remembering that UX design is a process that changes over time. What is designed exactly according to user requirements today may be obsolete tomorrow.
TAKE BUSINESS NEEDS INTO ACCOUNT
Users need products that meet their needs - that's a fact. But they also have expectations and business constraints. For example, a user may need your solution but have a specific budget. So the design team should focus on providing the customer with a product that fits their budget while meeting the minimum technical requirements.
Why does User Experience even matter?
In today's world, creating a product that solves a specific problem is not enough. It is also about creating an intuitive and pleasurable experience enhancing user satisfaction to the point that the user will want to return to the application. Therefore, UX design is a vital part of business development, and a few arguments support this statement.
Good UX design influences how quickly the user navigates the app.
To begin with, it is worth realizing that if we take proper care of UX design, we positively influence the user flow in our application. The solution becomes more intuitive, so users don't have to think about where to click on what and move more efficiently and quickly in the application.
The UX designer's role is to create an environment for target users in which they do not need to perform any unnecessary steps. The aim is to build a solution that enables a stress-free use of the application that allows users to achieve their goals.
Users stay longer with the app if happy - better conversion, ROI, and customer loyalty.
The design process adopts specific ideas about what is essential to user personas. It is a battle between a rich set of functionalities, an eye-catching design, and ease of use. And all of this must also, at the same time, work in tandem with the idea that the user should take a minimum number of steps to achieve their goal in the application.
UX design also undoubtedly involves the feelings and emotions of the user and is, therefore, of great importance in long-term user behavior. In the industry, there is the concept of Quality of Experience - a way of subjectively and objectively measuring user satisfaction.
Any brand that cares about a long-term product development strategy knows that if a product is easy to use and pleasant for the user and has an excellent feeling using it, they will return to the solution and stay there longer. That's why each company should prioritize the Quality of Experience as much as possible.
The premise that ties all of this together is simple - the happier the user is, the more likely they will stay with the app longer.
Further problems are prevented in advance - so we reduce potential costs.
Good UX design is an investment. Take the time in the beginning to find the right professional who understands UX design principles and conduct usability tests before launching a product. Then, you can save a lot in the future. In the UX design, we put the user and their needs first to minimize the likelihood that we will have to add something we might have missed.
UX design supports the brand reputation
A good product defends itself and strengthens the company that created it, as people judge a brand by the quality of what the company produces. Thus, UI (User Interface) supports the first impression, but UX design is already responsible for the long-distance maintenance of this impression.
Why is UX design important in software development?
Each specialist is primarily good in their field and may overlook aspects that other professionals take into account. The same is true for developers and UX designers.
If developers worked on products alone, they could create technically outstanding solutions. Still, they might need help with the user experience and requirements.
The development team can understand the user's needs, pains, and goals by working with UX designers.
What are the roles in the UX design process?
At the first glance, the UX design process may seem a bit complicated if you look at the people involved in creating the product. However, in understanding the different roles, it is crucial to know that each of these professionals has a specific contribution to the UX process.
So learning about such a role should start with understanding how that person contributes to the UX journey.
UX DESIGNER
It can be said that a UX designer is a person who does a little bit of everything in the UX process. Their job is to understand user needs, create solutions to solve problems, prototype designs, and go through testing with users. In short, the UX designer takes part in each stage of the design thinking process. This person doesn't have strong tech skills, but they should know UX design tools, understand how developers think, and have some knowledge concerning programming languages.
However, there is a difference between how the UX designer works in large organizations and small startups. In large companies, they work with other specialists, such as visual designers or UX researchers.
Smaller companies don't have such extensive teams, so the UX designer often handles all aspects of design.
In terms of nomenclature, you may also come across other names that are used to describe who the UX designer is:
- Experience Designer
- UI/UX Designer
- Interaction Designer
What tasks do they perform?
- Gather information through several different methods like observations and user interviews to find out what users like or dislike about the product.
- Use the data from the user research to find out what's not working for the users.
- Brainstorm and generate ideas to fix the identified problems.
- Make decisions based on various factors about which ideas will be implemented.
- Create designs from simple sketches to more advanced mockups.
- Being responsible for conducting user and usability tests to assess whether something needs improvement or change.
- Give the world a solution that will have a certain value for both the company and the users.
PRODUCT DESIGNER
One of the roles that have emerged relatively recently is the Product Designer. Its duties are close to what a UX Designer does, but unlike the former, it focuses more on the product itself. He helps with design and focuses on helping create the product roadmap and goals.
Because Product Designers' duties are similar to UX Designers, some companies view Product Designers as senior UX Designers who are also simply responsible for defining the product roadmap and product goals.
What are they responsible for?
They are responsible for the design process of almost all the same tasks as UX designers. At the same time, they are also involved in the following:
- Creating plans for the product roadmap.
- Working closely with the marketing and development team.
VISUAL DESIGNER
The next role is that of a specialist. The UX Visual Designer is the person who must design prototypes in a pixel-perfect way. An important part of such a person's job is to make sure their designs are in line with the rest of the project.
Their attention is devoted to the later stage of the design process. Other terms for this specialist you may encounter are Graphic Designer or UI Designer.
What tasks does the Visual Designer perform?
- Turns UX goals into actual user experiences.
- Creates a beautiful set of icons, graphics, fonts, and colors for the project.
- Uses brand guidelines when creating designs.
- Builds prototypes that are pixel-perfect and interactive.
- Collaborates with front-end developers to provide the development team with the design specifications required to implement the project.
UX RESEARCHER
Similar to a UX Designer, a UX Researcher is a specialist in their field. He or she does quantitative and qualitative research to gather real user feedback from users and thus contribute to the business making better decisions.
In addition, they have a say in which direction the functionalities will go, as he or she is involved in the testing phase and also helps to verify the functionalities.
What tasks does the UX Researcher do?
There is a whole set of activities that the UX Researcher performs:
- Uses different methods to learn about users, like user interviews and observations.
- Uses things such as sorting or surveys to gather information and specific traits of users.
- Examines the data they collect, and uses it to come up with important ideas for designing products.
- Carries out evaluative research methods, such as usability testing and user testing, to assess and enhance designs.
CONTENT STRATEGIST
A good UX product has more than a sleek and unique appearance or a well-thought-out path in terms of usability. The correct user experience also consists of words.
Since the copy is one of the essential parts of the UX design, the Content Strategist plays a critical role, especially in more complex organizations, which considerably impacts the final product.
What are the duties of the Content Strategist?
Content Strategist writes copy for the product. Examples include:
- Writing page titles and determining the naming of navigation menu titles to make it easier for users to get to different parts of the page.
- Creating error messages that, in an error situation, will not annoy the user but reinforce their sense of control.
- Creating emails and newsletters to support communication with users.
- Responsibility for the vision regarding the language used throughout the application.
UX UNICORN
In the world of tech startups, it is customary to use the word "unicorn" to describe someone who knows two different domains. UX Unicorn is, therefore, a unique position, combining two essential skills - UX and frontend development.
Such a person is responsible for the entire UX design process and can turn their design into actual code.
So what does a UX Unicorn do?
Everything that a UX Designer does, but in addition:
- Builds frontend prototypes so that the design's performance can be tested in more detail on users.
- Is responsible for implementing the frontend design code.
What does the UX design process look like?
The UX design process is a defined methodology for the various steps that must be followed to bring the project from A to Z according to the client's plan and expectations. It is an iterative process, so it is geared to take steps forward and go back to some elements that need to be changed. Depending on the organization and the type of product, the UX design process can vary a bit, but usually, companies use Design Thinking.
The classic UX design process consists of 6-10 stages. Below we will describe eight such steps.
Stage 1: You need to define the scope and project goals.
At this stage of the UX design process, you must define the project's scope with the other team members and key stakeholders. The team needs to know what problem this project is supposed to solve and what the execution plan, dates, and deliverables will be. Usually, people from the following departments are involved in this process:
- Business
- Product
- Design
- Technical
Step 2: You need to understand the problem
In the second stage, it is crucial to define the problem from the user's point of view. To achieve this, the team uses several tools to dig into what is essential and understand the problem to solve. A few examples can be:
- User personas
- Journey maps
- Empathy maps
Step 3: UX research needs to be done
In the next stage, designers do research to see how the problem set before them can be solved. A number of different methods are used at this stage, among which are:
User research - here, it is important to understand the customer well.
Market research - in this activity, it is important to know the market for the product.
Product research - this approach allows you to study an existing product to understand user behavior.
Competitive research - checking the competition to get an idea of what solutions are already being used in the market.
Stage 4: Ideation
At the stage where the information is already defined, designers can begin to act on the ideation phase. It is when many ideas are generated using a simple pen, pencil, and paper. The goal is to turn any such low-fidelity idea upside down if necessary and change the direction of thinking. Among the tools used are:
- Paper prototyping - paper product prototypes.
- Wireframing - paper prototypes turned into a digital version.
- Sketching - sketches user interfaces by hand.
- Low-fidelity prototypes - these are digital prototypes so you can check user flow.
- Design sprint is an intensive group session where the team can quickly solve a problem.
Stage 5: High-fidelity
At this stage, wireframes are converted into mockups. The goal is for high-fidelity prototypes to emerge, showing how the final product will look and work.
Stage 6: Usability testing
It is the stage at which high-fidelity prototypes are used to verify with users the following:
- Ideas - to verify if and which ideas make sense.
- Usability issues - to check if anything stands in the way of using the product.
- Accessibility - whether the application is adequately accessible.
- Business side - whether any other business opportunities are related to creating the solution.
It's also worth mentioning here that this is an iterative process. By validating the various elements, designers can return to earlier stages and make changes until the design conforms to critical, predetermined criteria. In addition to this process, during the entire UX design process, activities such as discussions with internal team members or key stakeholders also take place in the background to verify assumptions and resulting prototypes on an ongoing basis.
Stage 7: Handoff
It is the moment when the design team can finally hand over prototypes, mockups, and documentation to the development team so that the engineering process can begin. Although officially this moment occurs at stage 7, designers and the developers start working together much earlier, at the Ideation stage. The goal is to ensure that the engineers are versed in what is being created and that the emerging design meets the defined technical constraints.
Stage 8: UX Audit or Quality Assurance
It is the moment of truth, where the resulting product is verified and checked for user experience, business needs, and accessibility. It is also the moment when the team can check, based on real-world data, whether the user has any pain points and whether something can possibly be introduced to increase the solution's business value.
At the end of such a process, auditors create a report that includes information about the audit and possible recommendations for product changes or fixes. Depending on the type and size of the organization, such an activity may be performed by a team of designers, or, in the case of larger companies, a team of external specialists.
Summary
Nowadays, UX design is an integral strategic element in building products meant to meet users' expectations but also align with the business objectives of the creators. The process requires several stages, during which the design team and development, using specific tools, refine the product while giving themselves the freedom for iteration. Therefore, a good understanding of UX issues and the UX design process allows us to create better designs that not only grow the business but also help users solve problems that are important to them.